First Female Secretary of State
 Marie Jana Korbelova (1937-2022) was born in Prague to a Jewish family. Her father was a Czech diplomat and when Hitler occupied Czechoslovakia in 1938, the family fled and ended up in Britain. Traumatized by what they had experienced, and distraught over the loss of their parents and many other relatives in the Holocaust, the Korbels decided to convert to Catholicism and bury their Jewish identity for good. They did not tell their children that they were Jewish. After the war, the family return to Prague and Marie Jana went on to study in Switzerland, where she changed her name to Madeleine. When the Communists took over Czechoslovakia in 1948, the family fled again, this time to the US. Madeleine studied political science and wrote for The Denver Post, where she met her husband, journalist Joseph Albright. She went on to earn her Ph.D, focusing on the Soviet Union, and became fluent in Russian. In 1980, she was given a research grant at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars and explored Poland’s solidarity movement. She traveled across Poland for a long time and became fluent in the language. When she returned, Albright became a professor at Georgetown University, and also a foreign policy advisor for the Democratic Party. In 1993, Bill Clinton selected Albright to be the ambassador to the UN, and in 1997 she became the US Secretary of State, the first woman to hold the post and the highest-ranking women in the history of US government. One of her key moves was getting the US involved to stop the massacres in Bosnia, arguing that there was no point having a “superb military… if we can’t use it”. In 1998, she formulated NATO’s “3D” policy of “no diminution, no discrimination, no duplication”. After leaving government, Albright briefly served on the board of the New York Stock Exchange. Although she had been vocal about stopping Saddam Hussein back in the 90’s, she opposed the Iraq War. She ran a consulting firm, and also returned to teaching at Georgetown. Albright was awarded multiple honourary degrees and was inducted into the National Women’s Hall of Fame. Last year, she was on Forbes’ list of “50 Over 50” influential people. Altogether, she spoke 8 languages. Sadly, Madeleine Albright passed away last week after a battle with cancer.
Marie Jana Korbelova (1937-2022) was born in Prague to a Jewish family. Her father was a Czech diplomat and when Hitler occupied Czechoslovakia in 1938, the family fled and ended up in Britain. Traumatized by what they had experienced, and distraught over the loss of their parents and many other relatives in the Holocaust, the Korbels decided to convert to Catholicism and bury their Jewish identity for good. They did not tell their children that they were Jewish. After the war, the family return to Prague and Marie Jana went on to study in Switzerland, where she changed her name to Madeleine. When the Communists took over Czechoslovakia in 1948, the family fled again, this time to the US. Madeleine studied political science and wrote for The Denver Post, where she met her husband, journalist Joseph Albright. She went on to earn her Ph.D, focusing on the Soviet Union, and became fluent in Russian. In 1980, she was given a research grant at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars and explored Poland’s solidarity movement. She traveled across Poland for a long time and became fluent in the language. When she returned, Albright became a professor at Georgetown University, and also a foreign policy advisor for the Democratic Party. In 1993, Bill Clinton selected Albright to be the ambassador to the UN, and in 1997 she became the US Secretary of State, the first woman to hold the post and the highest-ranking women in the history of US government. One of her key moves was getting the US involved to stop the massacres in Bosnia, arguing that there was no point having a “superb military… if we can’t use it”. In 1998, she formulated NATO’s “3D” policy of “no diminution, no discrimination, no duplication”. After leaving government, Albright briefly served on the board of the New York Stock Exchange. Although she had been vocal about stopping Saddam Hussein back in the 90’s, she opposed the Iraq War. She ran a consulting firm, and also returned to teaching at Georgetown. Albright was awarded multiple honourary degrees and was inducted into the National Women’s Hall of Fame. Last year, she was on Forbes’ list of “50 Over 50” influential people. Altogether, she spoke 8 languages. Sadly, Madeleine Albright passed away last week after a battle with cancer.
When Madeleine Albright Found Out She’s Jewish
Russia, Ukraine, and the Coming of Mashiach
Words of the Week
Such is the way of fools: Once they achieve a little knowledge and awe, they think they have achieved a high level and don’t realize how ignorant they are.
– Rabbi Simcha Bunim of Peshischa

 Anatoliy Davidovich Daron (1926-2020) was born in Odessa, Ukraine. An avid pianist, he initially wished to become a musician. At age 12, he read a book about space and was inspired to become a rocket scientist, with the hopes of one day flying to Mars. That same year, World War II broke out and the family fled to Russia’s Stavropol region. A few years later, the Nazi invasion came to his town just as he was graduating high school—he got his diploma, written by the principal on a scrap piece of paper, while everyone was fleeing! Doron went on to study rocketry in Moscow, and soon joined OKB-456, the Soviet state institution tasked with missile and rocket development, under the leadership of Valentin Glushko. There, Daron worked on the USSR’s first intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). When the anti-Semitic
Anatoliy Davidovich Daron (1926-2020) was born in Odessa, Ukraine. An avid pianist, he initially wished to become a musician. At age 12, he read a book about space and was inspired to become a rocket scientist, with the hopes of one day flying to Mars. That same year, World War II broke out and the family fled to Russia’s Stavropol region. A few years later, the Nazi invasion came to his town just as he was graduating high school—he got his diploma, written by the principal on a scrap piece of paper, while everyone was fleeing! Doron went on to study rocketry in Moscow, and soon joined OKB-456, the Soviet state institution tasked with missile and rocket development, under the leadership of Valentin Glushko. There, Daron worked on the USSR’s first intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). When the anti-Semitic 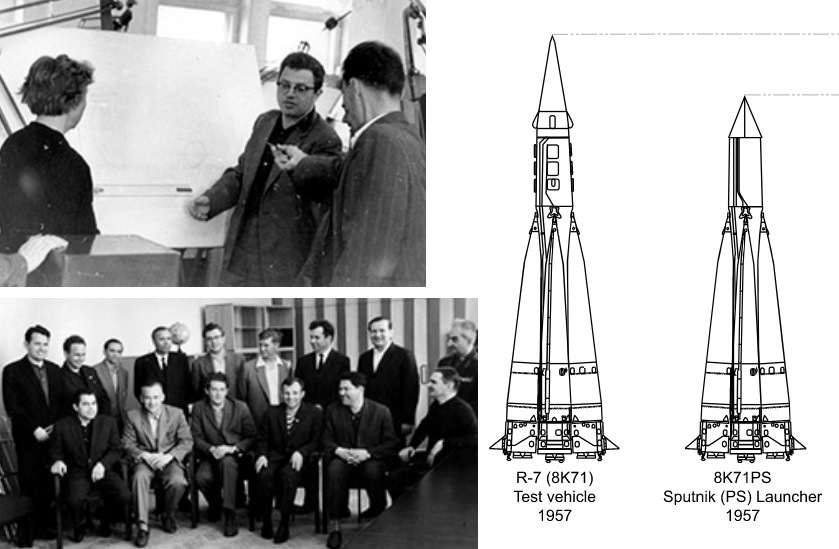
 Yitzhak Yezernitsky (1915-2012) was born in what is now Belarus and spent his youth in Poland. As a young man, he joined Betar, the Zionist organization founded by
Yitzhak Yezernitsky (1915-2012) was born in what is now Belarus and spent his youth in Poland. As a young man, he joined Betar, the Zionist organization founded by